Learning Cryptography
Cryptography - Caesar Cipher
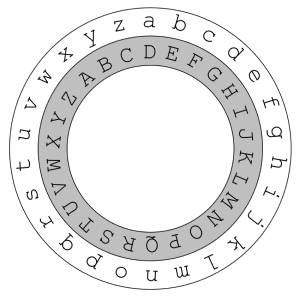
- The Caesar cipher (or Caesar code) is one of the simplest substitution ciphers, which encrypts plaintext by shifting the alphabet by a fixed number of positions.
-
The name of this cipher originates from the encryption method used by Julius Caesar in ancient Rome.
-
For example, if we shift the string ‘ABC’ by 3 positions, it becomes ‘DEF’. The alphabetical order must be maintained between the characters before and after the shift. Therefore, shifting ‘Z’ by 1 position should result in ‘A’.
- The Caesar cipher was widely used in ancient Roman times and was considered relatively secure at that time.
-
However, it can be easily decrypted using modern computers and brute-force attacks, making it an insecure encryption method.
- Nevertheless, the Caesar cipher is useful for understanding the basic concepts of cryptography, and various encryption methods have been developed based on its variations.
- For example, simply changing the shift value of 3 in the Caesar cipher for each encryption can easily increase the strength of the encryption.
- By applying these simple techniques, various encryption methods have been developed, which have served as the basis for more powerful encryption schemes.
| Plaintext | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n | o | p | q | r | s | t | u | v | w | x | y | z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ciphertext | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | A | B | C |
Code
1
2
3
4
5
pub fn encryption(
string: &str, // The string to be encrypted
shifts: u8, // The shift value used in the Caesar cipher
lang_arr: Vec<char>, // The character set to be used
lang_arr_upper: Vec<char>, // The array of characters used to maintain the order of lang_arr
- string: The string to be encrypted.
- shifts: The shift value used in the Caesar cipher.
- lang_arr: The character set to be used.
- lang_arr_upper: The array of characters used to maintain the order of lang_arr.
1
Result<String, Box<dyn std::error::Error>>
- The function returns a Result<String, Box<dyn std::error::Error». If the returned value is Ok, it contains the encrypted string; if it is Err, it contains an error of a subtype of std::error::Error.
1
let letters: HashMap<usize, &char> = lang_arr_upper.iter().enumerate().collect();
- Create a HashMap called letters that stores the index of each character by enumerating lang_arr2.
1
2
3
4
5
let numbers: HashMap<char, usize> = lang_arr
.iter()
.enumerate()
.map(|(idx, chr)| (chr.clone(), idx))
.collect();
- Create a HashMap called numbers that stores each character and its index by enumerating lang_arr.
1
2
3
Ok(string
.chars()
.map(|c| {
- Convert the string to an iterator of char type using the chars() method.
-
- Use the map() method to perform the Caesar cipher on each character of the string.
1
2
if c == ' ' {// * If the character is a space, return it as is.
c
-
- If the character is a space, return it as is.
1
2
3
4
5
6
let shift = numbers[&c] + shifts as usize;
//* If the index after shifting exceeds the range of lang_arr, use the letters HashMap to wrap around the alphabet.
if shift > lang_arr.len() - 1 {
// Change the letter shift to the remainder of the array size
*letters[&(shift % lang_arr.len())]
-
- If the character is an alphabet, use the numbers HashMap to obtain the index of the character and shift it by shifts.
1
if shift > lang_arr.len() - 1 {
-
- If the index after shifting exceeds the range of lang_arr, use the letters HashMap to wrap around the alphabet.
1
2
3
4
else {
// If wrapping around is not necessary, use the letters HashMap to convert the index to a character
*letters[&shift]
}
-
- If wrapping around is not necessary, use the letters HashMap to convert the index to a character.
1
.collect::<String>())
- Use the collect() method to generate the encrypted string.